[ad_1]
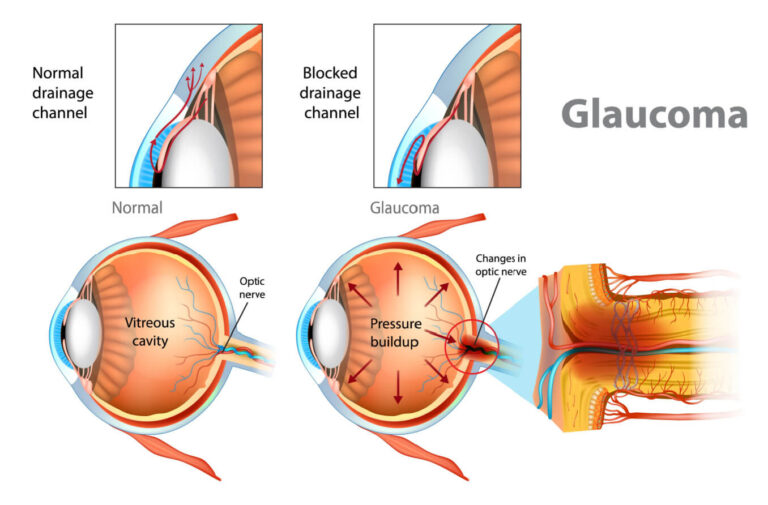
Glaucoma is a serious eye condition that can lead to irreversible vision loss if left untreated. It is often referred to as the “silent thief of sight” because it typically has no noticeable symptoms until it has already caused significant damage to the optic nerve. Understanding the risk factors and symptoms of glaucoma is crucial for early detection and treatment.
Risk Factors for Glaucoma:
– Age: People over the age of 60 are at a higher risk for developing glaucoma.
– Family history: If you have a family member with glaucoma, you are at a higher risk of developing the condition yourself.
– Ethnicity: African Americans, Hispanics, and Asians are at a higher risk for glaucoma compared to Caucasians.
– High eye pressure: Elevated intraocular pressure is a major risk factor for glaucoma.
– Diabetes: People with diabetes are at an increased risk for developing glaucoma.
– Myopia: Severe nearsightedness is associated with a higher risk of glaucoma.
– Previous eye injuries or surgeries: Eye trauma or surgery can increase the risk of glaucoma.
Symptoms to Watch For:
– Vision loss: Glaucoma typically causes peripheral vision loss first, which can progress to tunnel vision and eventually complete blindness if left untreated.
– Blurred vision: If you experience sudden or gradual blurriness in your vision, it may be a sign of glaucoma.
– Eye pain or redness: Persistent eye pain or redness can be a symptom of acute angle-closure glaucoma, a medical emergency that requires immediate treatment.
– Halos around lights: Seeing halos around lights, especially at night, can indicate elevated eye pressure.
It is important to note that many people with glaucoma do not experience any symptoms until the condition has progressed to an advanced stage. This is why regular eye exams are crucial for early detection and treatment of glaucoma.
If you have any of the risk factors for glaucoma or are experiencing any of the symptoms mentioned above, it is important to schedule an eye exam with an optometrist or ophthalmologist. During the exam, the eye doctor will measure your intraocular pressure, examine the optic nerve, and perform other tests to determine if you have glaucoma.
Treatment for glaucoma typically includes eye drops to lower intraocular pressure, laser therapy, or surgery in more severe cases. Early detection and treatment of glaucoma can help preserve your vision and prevent permanent vision loss.
In conclusion, understanding the risk factors and symptoms of glaucoma is key to early detection and treatment of this sight-threatening condition. By being proactive about your eye health and scheduling regular eye exams, you can protect your vision and reduce your risk of developing glaucoma.
[ad_2]