[ad_1]
Hepatitis B is a viral infection that affects the liver and can cause both acute and chronic illness. It is one of the most common infectious diseases in the world, with an estimated 257 million people living with chronic hepatitis B infection globally.
Causes of Hepatitis B:
Hepatitis B is caused by the hepatitis B virus (HBV), which is transmitted through contact with the blood or other body fluids of an infected person. The most common modes of transmission include:
– Unprotected sex with an infected partner
– Sharing needles or syringes with an infected person
– From mother to baby during childbirth
– Sharing personal items such as razors or toothbrushes with an infected person
– Healthcare workers exposed to infected blood or body fluids
Symptoms of Hepatitis B:
Many people with hepatitis B do not experience any symptoms and are unaware that they have the virus. However, some individuals may develop symptoms that can range from mild to severe. Common symptoms of acute hepatitis B include:
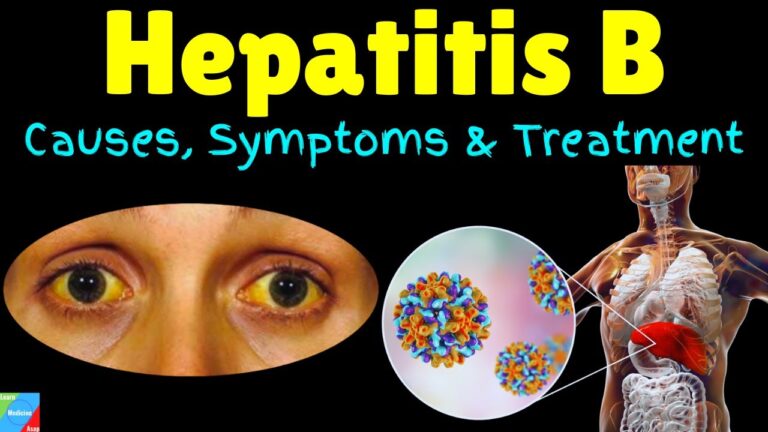
– Jaundice (yellowing of the skin and eyes)
– Fatigue
– Nausea and vomiting
– Abdominal pain
– Dark urine
– Clay-colored stools
– Fever
– Joint pain
Chronic hepatitis B can lead to more serious complications such as liver cirrhosis, liver cancer, and liver failure. It is important to seek medical attention if you experience any symptoms of hepatitis B, especially if you have been exposed to the virus.
Treatments for Hepatitis B:
There is no cure for hepatitis B, but there are treatments available to help manage the virus and prevent complications. The most common treatment for chronic hepatitis B is antiviral medication, which can help to lower the viral load in the body and reduce the risk of liver damage.
In some cases, a liver transplant may be necessary for individuals with advanced liver disease caused by hepatitis B. It is important to work closely with a healthcare provider to monitor the progression of the virus and determine the most appropriate treatment plan.
Prevention of Hepatitis B:
The best way to prevent hepatitis B is through vaccination. The hepatitis B vaccine is safe and effective, and is recommended for all infants, as well as adults at risk of exposure to the virus. In addition to vaccination, practicing safe sex, avoiding sharing needles or other personal items, and getting tested for hepatitis B can help prevent the spread of the virus.
Understanding hepatitis B is crucial for preventing and managing the virus. By knowing the causes, symptoms, and treatments for hepatitis B, individuals can take the necessary steps to protect themselves and others from this potentially serious infection.
[ad_2]